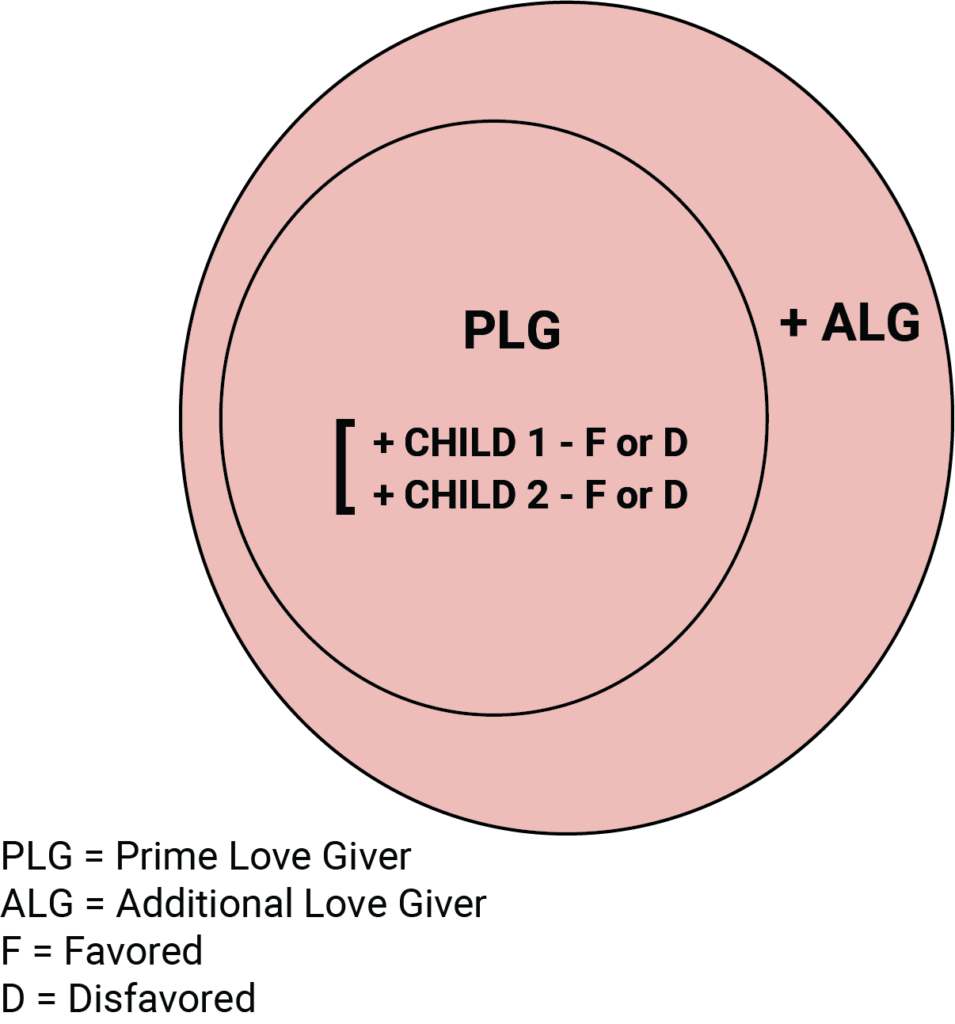
DOLF follows the flow of Emotions, specifically MORE LOVE and LESS LOVE, starting with the basic model of a family with two parents and two children. In DOLF the standard pattern in any family is that one of the first two children forms a strong, LOVING bond with the more Emotionally accessible Prime Love Giving parent, or PLG. This child, whether the first or second, becomes the Favored one of the first two siblings, and the LOVE dynamic between this child and the PLG parent results in this child forming a lovable, easy-going personality and a positive behavioral style. At the same time the adjacent sibling develops a less loving Emotional bond with the PLG and feels less loved or Disfavored by comparison. As a result this child develops a contrasting negative personality and behavioral style that is infused with Anxiety, Depression and Anger. As shown in the diagram below, either one of the first two children, whether the first- or second-born child, can turn out to be the Favored or the Disfavored one:
When a third child is born, the first two siblings remain the same as ever in their personalities and interactions. The possible personalities and patterns of interaction that evolve are described in the blog More Kids – The Third Child, as well as in another blog titled Third Child Concerns that outlines some dangers to mental health that a third child might face.
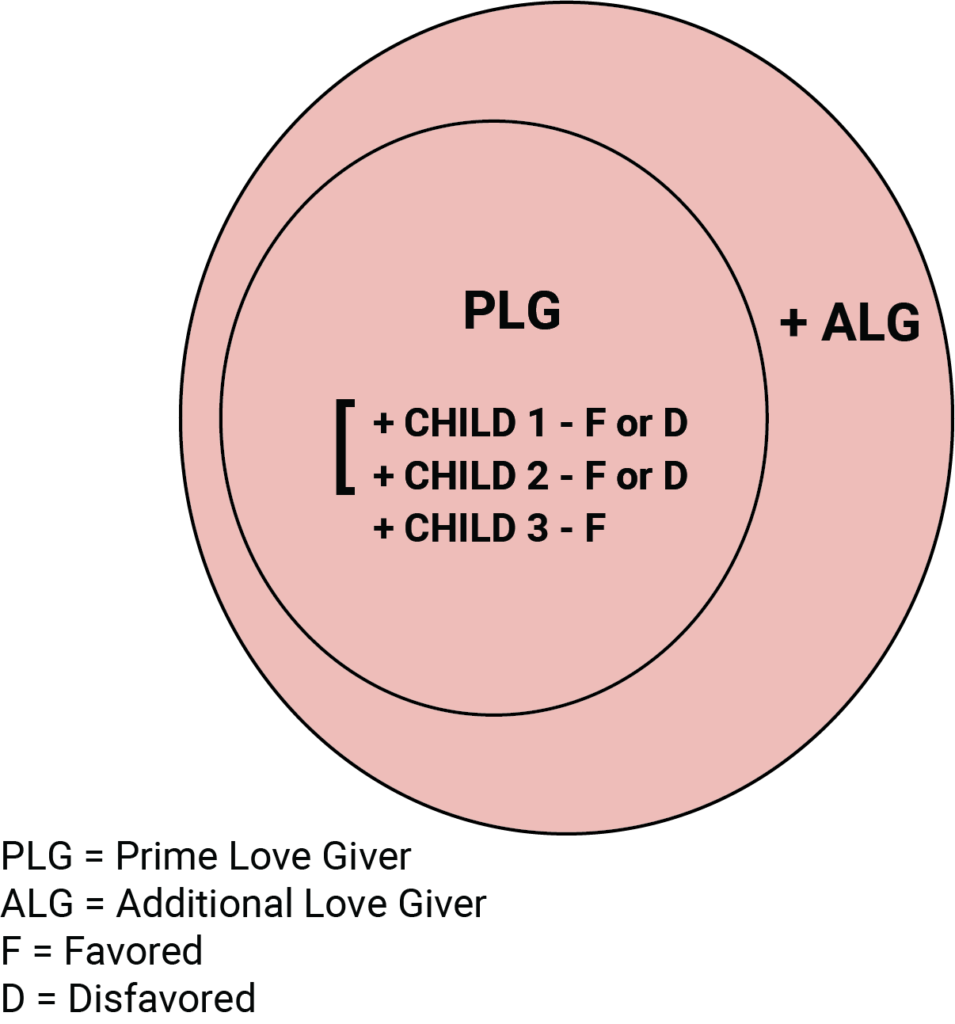
As a general rule, a third child does NOT participate in the ongoing SIBLING RIVALRY between the first two. As well, unless otherwise specified for any reason, a third child is always assumed to be of a Favored temperament, as illustrated below:
The Fourth Child
When a fourth child is added to the family, this fourth child competes with the third one to form a new cluster or grouping that consists only of the last two children. This new grouping now operates separately from the first group. The original Sibling Rivalry grouping between the two older siblings remains undisturbed and the same in style and intensity. The main change to the family is that another rivalrous cluster or subgroup has been added that consists of the last two children. As illustrated below, Child 3 now sees Child 4 as their own direct competitor and they gravitate toward each other to form this new grouping. Both these younger siblings immediately perceive each other as competitors and begin to carry on their own SIBLING RIVALRY exclusively with one another in the same way as the older two did.
Specifically on a psychological level, these groupings or clusters operate independently. This means that Child 1 does NOT compete with 3 or 4, and equally Child 2 does NOT compete with 3 or 4. In other words, the participants of each group only see the participants of their own group as their direct competitors. Any gestures the children might make, such as Child 1 or 2 picking on and fighting with one or other of the younger siblings, is simply a decoy that fools its observers. If an older sibling is reaching out of their own grouping and tormenting a younger child in the lower group, it indicates that this older child is frustrated with her/his inability to break into the powerful Emotional bond between their own competitor (Child 1 or 2) and their PLG parent.
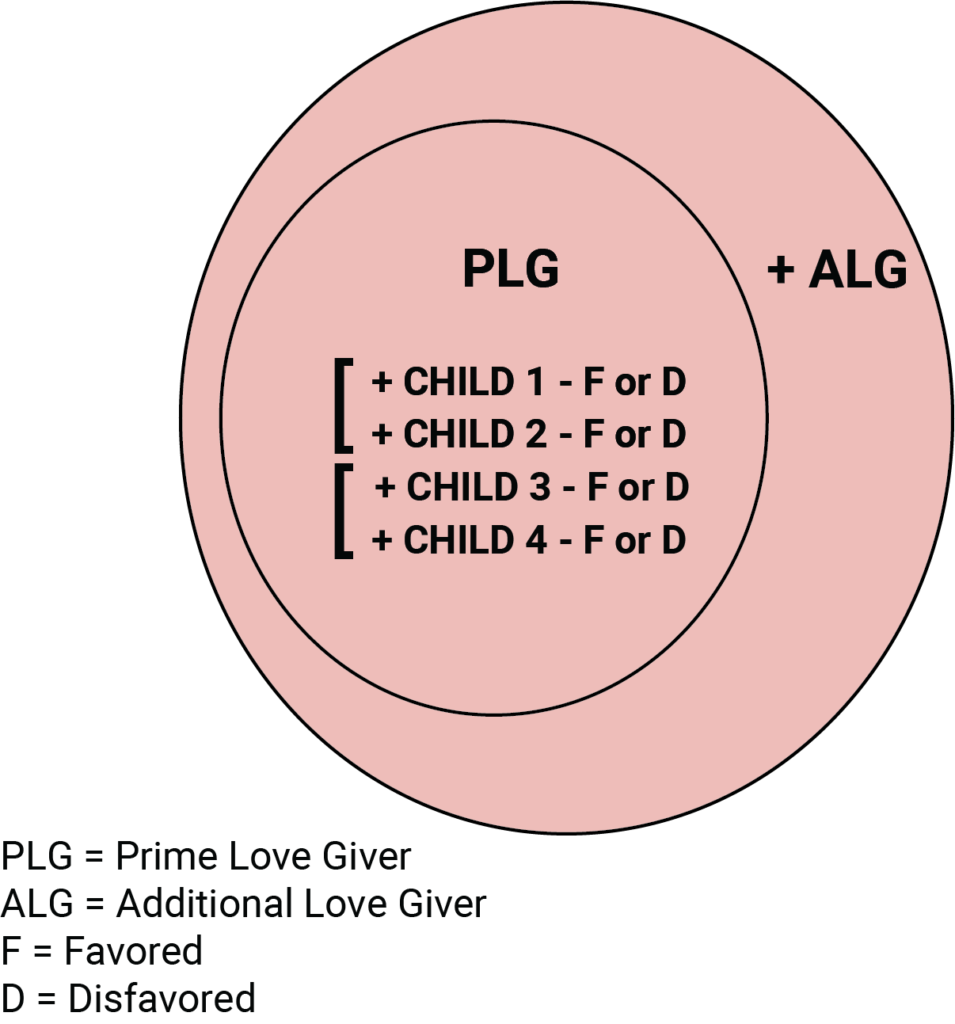
With the arrival of the fourth sibling, the same Emotional dynamics are repeated. Just as in the first group, one of the children from this new group, whether Child 3 or Child 4, forms a stronger Emotional bond with the PLG, while the other forms a weaker Emotional bond with the prime parent. As a consequence in this second group too there will emerge one sibling who is Favored and the other who is Disfavored. And again as with the first group, though the choice is random as to age, it is predictable as to behavior. That is, it can be either the older or the younger child in this new grouping who will ultimately succeed in attracting the LOVE of the PLG. The result is that either Child 3 or 4 will become the Favored sibling with the positive personality style, while the other child will have a more distant attachment to the PLG, become Disfavored by comparison, and develop a ‘negative’ personality style infused with Anxiety, Depression and Anger. In other words, the same rules apply to this younger grouping as applied to the two older siblings. So in this 4-sibling family there are now two groups of siblings who compete within their own 2-sibling group, giving rise to two Favored children and two Disfavored children.
In this 4-sibling family, the PLG parent of the second group always remains the same. This parent is the original PLG who was chosen when the family first started, and is the same parent who bonded with the first child early in the life of that family. A firm rule in DOLF is that once two parents are established as PLG and ALG, which takes place as soon as their first child is born, the parental positions never change no matter how many more children come along. The PLG and ALG remain in their initial roles – the ones they assumed when their first child arrived, and these role divisions among the parents will continue for the remaining life of the family regardless of how many more children are added.
This format of 2 older plus 2 younger children in a family of 4 siblings is a standard pattern. We do NOT have to think twice. It is fixed and unchangeable, so that every time we find a 4-sibling family, the likelihood that the children will separate this way and compete in two groupings of two adjacent siblings is, for all practical purposes, 100%. Strange as it might look to us, the pattern occurs reliably and without fail in every 4-child family as soon as the fourth child is born. Like the formulae for two and three children, these group patterns are fixed and tend to present very little room for variation. It is then up to parents and professionals to figure out the true dynamics behind their family situations and check exactly how they play out within their own family settings.

